Context Search Engine
Project Overview
The Context Search Engine is an AI-powered semantic document search platform that demonstrates the full pipeline from document ingestion to context-aware query results using modern vector search. It is designed as a learning and experimentation lab for students, researchers, and developers who want to understand how semantic search works beyond simple keyword matching.

The system processes documents (PDF, DOCX, TXT), chunks them intelligently, converts text to embeddings using transformer models, and performs similarity search using FAISS. Unlike traditional keyword search, this semantic approach understands meaning and context, returning conceptually related results even when exact words don't match.
Technical Architecture
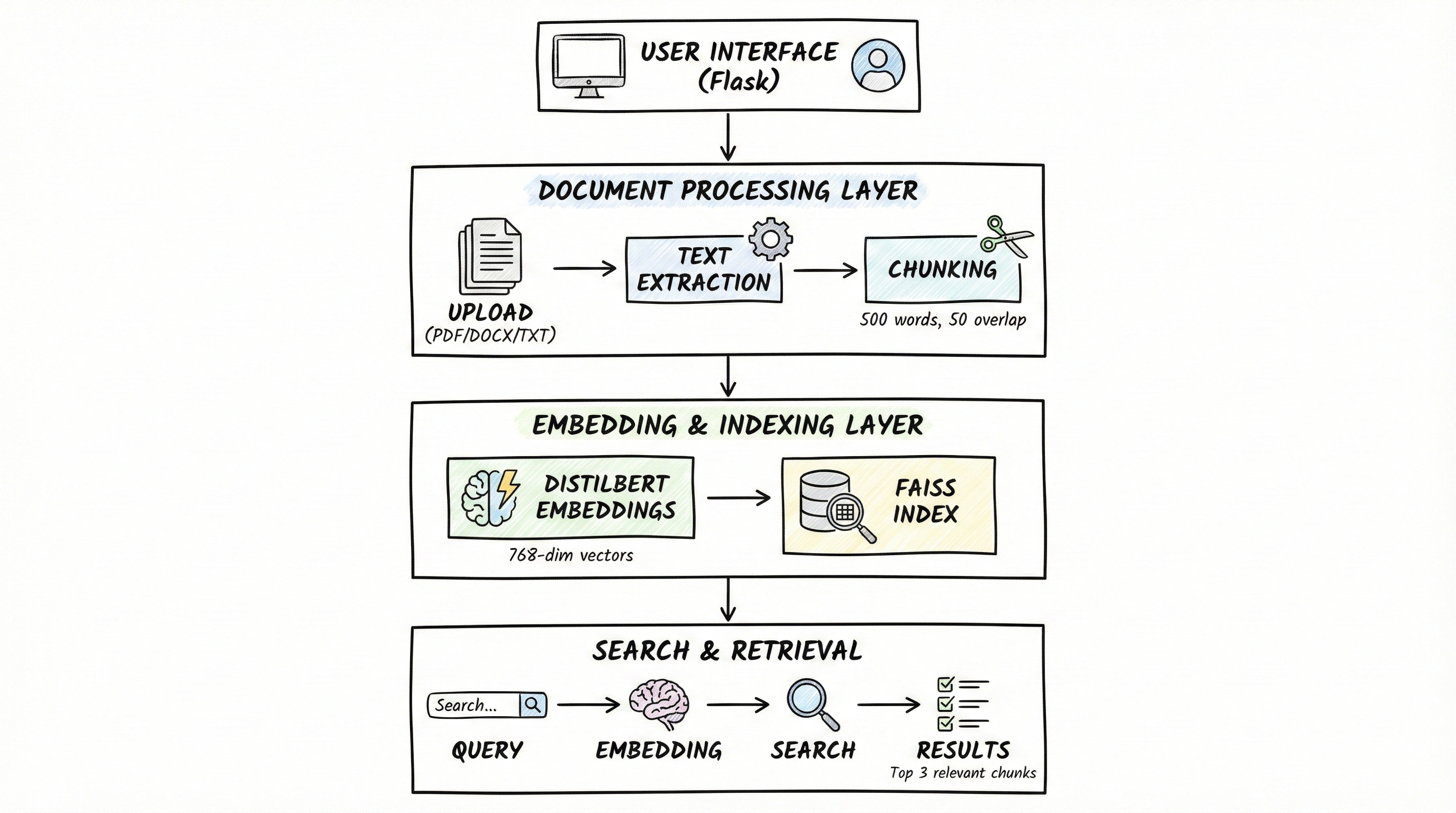
Document Upload → Text Extraction → Chunking → Embeddings → FAISS Index → Semantic Search
Key Components
NLP & Embeddings
Vector Search
Document Processing
Implementation Details
The core logic of the system can be summarized as: configurable chunking → embedding with a transformer model → FAISS similarity search over chunk vectors. Below is a simplified implementation:
from pathlib import Path
from typing import List, Dict, Any
import faiss
import numpy as np
from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModel
import torch
class SemanticSearchEngine:
def __init__(self, model_name: str = "distilbert-base-uncased", dimension: int = 768):
self.model_name = model_name
self.dimension = dimension
# Load embedding model
self.tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name)
self.model = AutoModel.from_pretrained(model_name)
# Initialize FAISS index
self.index = faiss.IndexFlatL2(dimension)
self.metadata: Dict[int, Dict[str, Any]] = {}
self._next_id = 0Chunking & Embedding Process
Documents are split into overlapping chunks to preserve context, then converted to embeddings using mean pooling over transformer outputs:
def _simple_chunk(self, text: str, chunk_size: int = 500, overlap: int = 50) -> List[str]:
words = text.split()
chunks = []
start = 0
while start < len(words):
end = start + chunk_size
chunk_words = words[start:end]
chunks.append(" ".join(chunk_words))
start += max(chunk_size - overlap, 1)
return chunks
@torch.no_grad()
def _embed_texts(self, texts: List[str]) -> np.ndarray:
inputs = self.tokenizer(texts, padding=True, truncation=True, return_tensors="pt")
outputs = self.model(**inputs)
# Mean pooling over token embeddings
embeddings = outputs.last_hidden_state.mean(dim=1)
embeddings = embeddings / embeddings.norm(dim=1, keepdim=True)
return embeddings.cpu().numpy().astype("float32")Project Results
System Capabilities
| Feature | Description | Status |
|---|---|---|
| Semantic Search | Context-aware query results beyond keywords | ✅ Live |
| Document Processing | PDF, DOCX, TXT with metadata extraction | ✅ Live |
| Configurable Pipeline | Adjustable models, chunk size, overlap | ✅ Live |
| Index Management | FAISS-based vector storage & search | ✅ Live |
Live Demo
Try Context Search Engine
Upload your documents and experience semantic search that understands meaning, not just keywords!
Challenges & Solutions
Document Boundary & Context Loss: Splitting long text into chunks can cut important context. Solved by implementing configurable chunk size and overlap, ensuring that information near boundaries is present in multiple chunks, preserving semantic continuity across splits.
Model Compatibility & Dimensions: Different models output different embedding dimensions; FAISS index must match. Solved with explicit dimension parameter in configuration, validated when building the index. UI prompts users to rebuild when changing model or dimension.
Balancing Speed vs Quality: Larger models and higher top_k values improve quality but cost time. Solved with configurable model, top_k, and num_search_results, allowing users to empirically find optimal trade-offs for their specific use case and corpus size.
Future Enhancements
- Version 2.1: Multi-user support with authentication, document folders, search history, and export results
- Version 2.2: Batch upload, advanced filters (date, type, tags), text highlighting, and query suggestions
- Version 3.0: Full RESTful API, Docker support, cloud deployment templates (AWS/GCP/Azure), analytics dashboard
- Long-term: GPU-accelerated FAISS, incremental indexing, hybrid search (keyword + semantic), and OCR integration
- Multilingual support for both UI and search capabilities